Basic HTML Version

8
9
Free route airspace
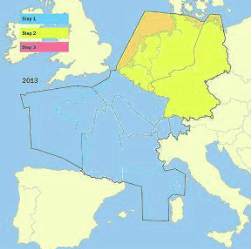
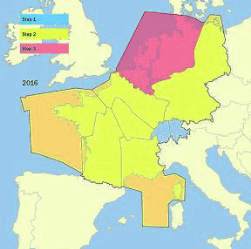
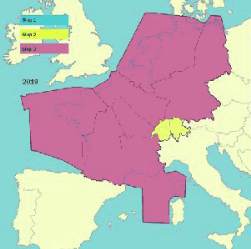
One of the main parts of the airspace strategy is the implementation of Free Route Airspace. The FABEC Free
Route airspace will cover the whole airspace from the western coast of France to the border of Germany and
Poland – from the Mediterranean Sea to the North Sea. It has been agreed that the minimum level will be FL365
FABEC-wide, but wherever possible it will be implemented at altitudes as low as possible. Based on one common
operational free route concept valid for all ANSPs a detailed roadmap was developed. The implementation is
scheduled stepwise from 2012 onwards starting at night and at weekends. In a second step, it will also be used
during military activities; the last step will be the use of business trajectories. Free route airspace is a specified
airspace within which users may freely plan a route between a defined entry point and a defined exit point,
with the possibility to route via waypoints, without reference to the ATS route network, subject to airspace
availability. In contrast to the free flight concept, all flights remain subject to air traffic control.
Initial steps are already taken in the Maastricht and
Karlsruhe centres. Maastricht introduced free route
airspace at the end of 2010 when 115 new night time
routes were created within FABEC airspace. In early
2011 MUAC created 142 direct routes and extended
the service to weekends at the end of the year. If
airlines used every free route opportunity, MUAC
estimates they would save 3,700 tonnes of fuel and
shorten flights paths by km 720.000 NM per year
compared to the fixed route network. Karlsruhe
already offers 150 direct routes above FL345 in
Germany’s less dense eastern airspace on a 24 hour
basis, offering potential savings of 850,000 nm a year
for airspace users. The procedures are supported by
the new P1/Vaforit flight processing systemwhich
supports four-dimensional trajectory prediction and
electronic data transfer with the advanced flight
data processing system at MUAC. Meanwhile the first
cross-border free routes are due to be introduced
between MUAC and Karlsruhe control centre in 2012.
Articles
Articles
FABEC
Peter van Hoogstraten, FABEC Chairman Standing Committee Operations
In January 2012 FABEC ANSPs agreed on a common
airspace strategy. Best practices like the night
network, Arrival Management Systems in Amsterdam
and Frankfurt, Airport-CDM in Paris and Munich and
initial steps of free route airspace structure
implemented in Maastricht and Karlsruhe were taken
on board, examined by operational experts and
streamlined to a FABEC Airspace Strategy. It includes
two new initiatives: the implementation of free route
airspace and the development of an Extended Arrival
Management (XMAN).
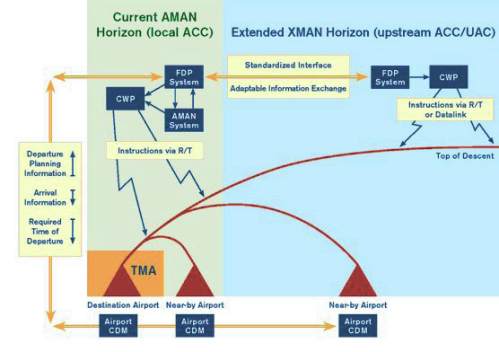
Extended Arrival Management
To improve flight efficiency by enhancing the scope
of continuous decent operations (CDO), FABEC will
develope an Extended Arrival Management function
(XMAN) focussing on the five major airports Paris,
Frankfurt, Amsterdam, Munich and, due to its
influence on FABEC operations, London. XMAN
encompasses the integration/connection of individual
Arrival Management Systems into one FABEC Concept
of Operations allowing optimization of existing traffic
streams. In addition, and based on its open concept
XMAN will be extended to other major airports
in the FABEC area. Instead of the limited range of
existing intra-centre arrival management systems,
XMAN will allow the planning of arrivals across centre
boundaries within a range of approximately 200
nautical miles.
To safe costs XMAN is based on existing technologies.
XMAN uses OLDI data-exchange – more specific the
AMA message. Amsterdam and Maastricht have
already been using the tool since December 2011.
AMA messages are sent electronically from
Amsterdam to the Maastricht ATC system containing
essential information for managing air traffic inbounds
to Schiphol. The data received enables air traffic
controllers in Maastricht and Amsterdam to issue
speed instructions at an early stage during the
descent to destination. This results in a streamlined
amount of traffic, improves flight efficiency, and
results in savings fuel per flight affected. It’s expected
that most other AMAN implementations in the
FABEC-area will be in place by 2015. Since arrival
management and departure management (DMAN)
are linked via Airport-CDM (Collaborative Decision
Making), this has also been included. FABEC plans on
implementing Airport-CDM FABEC-wide on the basis
of the respective specification of the European
Commission.
ANSPs agreed on common Airspace Strategy
“One main part
of the airspace
strategy is the
implementation
of Free Route
Airspace.“

